Everything You Need to Know AboutPeri-implantitisorImplantsFrom Symptoms to Treatment
Dental Implantis a cosmetic method and an effective solution for replacing lost teeth, but it can come with difficulties like peri-implantitis.
In this condition, inflammation occurs in the soft and hard tissues around the implant, affecting the bone supporting tissue, leading to progressive bone structure degradation responsible for keeping the implant in place.
In this section about oral and dental healthSelMagzwe will discuss the causes and symptoms of this issue. We will also tell you how to treat this condition.
Causes of Peri-implantitis
Bone loss around the implant can happen for various reasons. There are also two main etiological causes of peri-implantitis:
- Bacterial problems caused by bacteria accumulation from the mouth on the surface of the implant.
- Pressure created during implant placement can cause breakage and lead to this condition, usually occurring when the implant site is incorrect or when the applied force is not balanced.
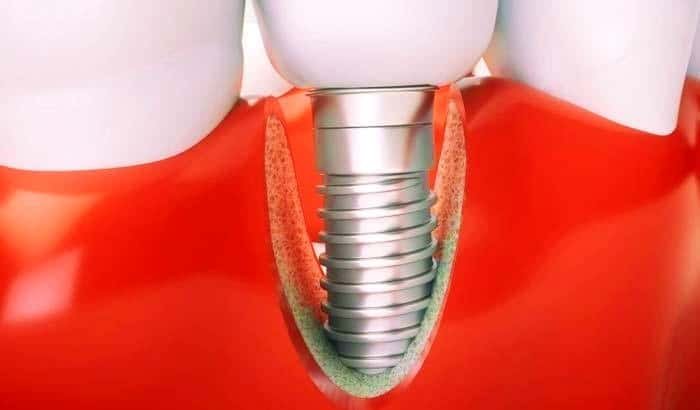
Causes and Risk Factors of Implantitis
As mentioned earlier, peri-implantitis occurs due to bacterial accumulation. There are other factors that can contribute to this condition:
– Patient’s hygiene habits, genetic conditions, or any existing problems can cause this issue.
The dentist must review the situation before the implant. Accurate diagnosis and evaluation of bone and gums are crucial to prevent it.
Risk Factors for Peri-implantitis
Some risk factors for peri-implantitis include:
- Smoking
- Poor quality of supporting bone for the implant
- DiseasesPeriodontal issues
- Systemic diseases likeOsteoporosis
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Poor oral hygiene
- The presence of bacteria during implant placement
- Poor pressure distribution during the implant process
- Stress

What are the Symptoms of Peri-implantitis?
The symptoms of this condition resemble periodontal disease in natural teeth. As mentioned before, they relate to inflammation of the tissues surrounding the implant.
Usually, a bacterial plaque or tartar, or the swelling or redness of mucous membranes around the implant causes this condition. Additionally, bleeding can occur while brushing, flossing, or during procedures in this area.
Sometimes wounds or pus appear in this area, especially if the cavity exceeds 6 millimeters.
X-rays may reveal issues with the bone tissue. In fact, an implant may indicate the progression of this condition. Moreover, this condition typically does not cause pain, although some patients may feel discomfort while chewing.
A person with this condition should see a dentist promptly. The sooner this condition is addressed, the better the outcome will be.
Regular checkups after implant placement are crucial because few people notice this issue themselves; therefore, checkups can help with early detection.
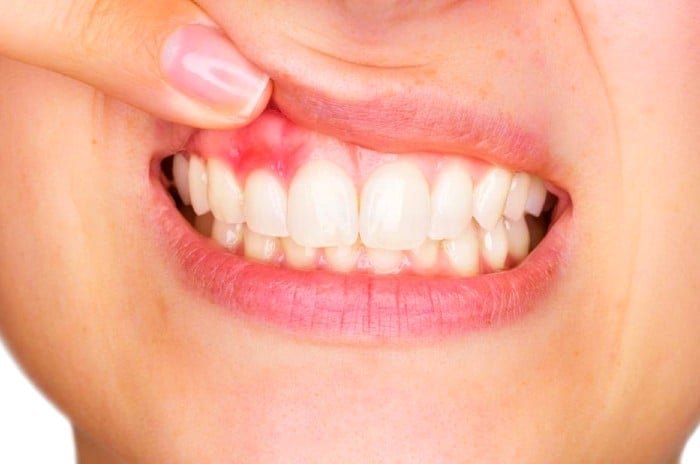
Diagnosis of Peri-implantitis
As mentioned earlier, regular checkups and dentist visits can help evaluate the conditions of the tissues around the implant and the dental plaque levels in the mouth, preventing the progression of this condition as quickly as possible.
The diagnostic process focuses on identifying changes in the soft tissue and the bone surrounding the implant. Clinical tests and measuring the depth of the cavity created for the implant can detect any inflammation, bleeding, pus, and implant movement.
X-rays are also considered essential, as they allow for analysis of bone density.
Treatment Options for Peri-implantitis
Treating this condition involves controlling the infection to stop damage and bone loss. The dentist can find the most effective treatment option based on the severity of the condition for you.
Antibioticsmay also be prescribed for treating the infection, which can be oral or topical.Sometimes, a device may be placed in the oral cavity to suction out infections, and additionally, the gum tissue may be manually separated to reduce inflammation and speed up recovery.
If this condition has caused bone loss, surgery may be performed. There are various types of surgery you can choose from based on your needs and the doctor’s diagnosis.
During surgery, the damaged area is opened to remove diseased tissue and disinfect the site. Typically, specific features of the bone and soft tissue are altered to prevent new plaque formation.
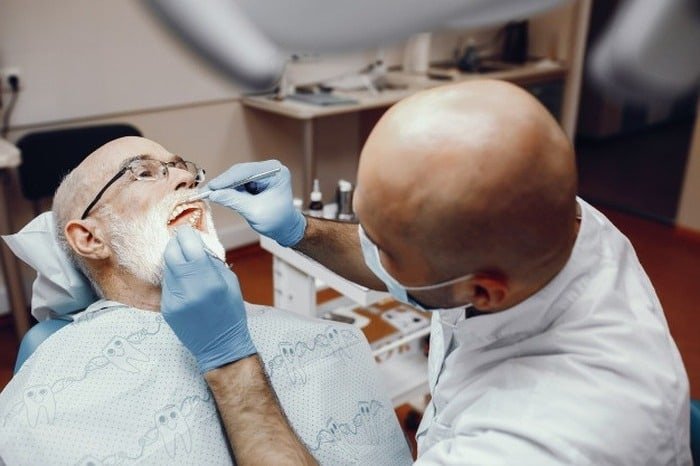
In some procedures, a displacement in membranes may occur to allow recovery of lost bone.
In addition to all these actions, the individual’s oral hygiene must be improved; thus, the doctor will provide instructions for maintaining clean teeth.
A specialist may also recommend using disinfectant cleaners to minimize the likelihood of bacterial formation. Only a specialized dentist can determine which treatment works best for you.
Caring for Implants or Peri-implantitis
Some uncontrollable factors may increase the likelihood of developing this condition; therefore, caring for the implant after surgery can reduce risks and difficulties, making oral hygiene the most essential practice to maintain.
- Brush your teeth at least three times a day and after every meal to prevent the accumulation of bacteria that cause post-implant issues.
- Also, pay special attention to hard-to-reach areas while brushing to clean around all your teeth.
- Maintaining hygiene with
- dental flossor mouthwashes is very helpful.Smoking increases the risk of peri-implantitis and exacerbates inflammation and decreases bone density.
- Additionally,
- bruxismdue to stress can worsen this condition.Most importantly, regular checkups with the dentist can identify the problem as soon as possible, allowing for quicker and better treatment.
- Peri-implantitis







